
Image Source: ATToday
Navigating the world can be challenging for individuals who are blind or have low vision. The WeWalk smart cane enhances traditional mobility tools with advanced technology, offering greater independence and ease. In this blog, we explore the key features of WeWalk and how it aligns with different models of disability.
What is Assistive Technology (AT)
Assistive technology (AT) is any item, piece of equipment, software program, or product system that is used to increase, maintain, or improve the functional capabilities of persons with disabilities. AT can range from physical tools like hearing aids to digital technologies like screen readers. The primary goal is to remove barriers, increase independence, and empower users to navigate the world more effectively.
What is WeWalk and how does it function?
WeWalk is a smart cane designed for individuals who are blind or have low vision, created by the Turkish startup WeWalk, co-founded by Kürşat Ceylan, who has been blind since birth. It’s an example of assistive technology that enhances the traditional white cane with ultrasonic sensors, haptic feedback, and GPS technology. These features provide users with added support to navigate their surroundings safely and independently.

Image Source: WeWalk Youtube
The WeWalk cane uses ultrasonic sensors to detect obstacles at head height, sending vibrations through the handle to alert users. It also syncs with a smartphone app for real-time GPS navigation, offering turn-by-turn directions, route planning, and nearby points of interest. This integration of technology into a traditional mobility tool improves accessibility, safety, and autonomy for people with visual impairments.
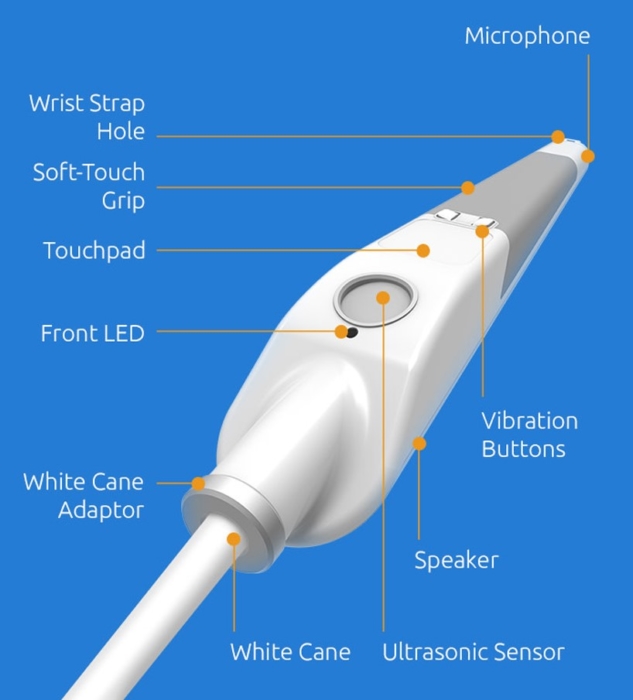
Image Source: Assistive Technology at Easter Seals Crossroads
Key features of WeWalk Smart Cane
1. Obstacle Detection with Ultrasonic Sensors
WeWalk’s ultrasonic sensors detect obstacles at head height, unlike traditional canes, which only detect obstacles at ground level. When an obstacle is detected, the cane vibrates to alert the user. This feature helps blind or low-vision individuals navigate spaces with overhead obstacles, improving safety and independence.
This feature aligns with the Social Model of Disability, which suggests that disability results from the interaction between individuals and a society that doesn’t accommodate them. WeWalk helps overcome environmental barriers, allowing users to move freely in spaces not designed with accessibility in mind. For blind individuals, this feature offers a greater sense of autonomy, overcoming limitations present with traditional white canes.
2. Haptic Feedback for Navigation
WeWalk provides haptic feedback through vibrations to guide users during navigation. These vibrations signal when a turn is necessary or when an obstacle is nearby. This non-visual, tactile system helps users orient themselves in both familiar and unfamiliar spaces.
This feature ties into the Medical Model of Disability, which addresses specific impairments. In this case, the haptic feedback compensates for vision loss by providing a tactile alternative for navigation. For blind people, it enhances mobility and independence, reinforcing that blindness does not restrict their ability to interact with the world around them.
3. GPS Integration for Turn-by-Turn Directions
WeWalk integrates GPS functionality, offering turn-by-turn navigation via a smartphone app. This feature gives users real-time guidance, especially in unfamiliar environments, promoting independence and reducing reliance on others for directions.
This feature connects to the Social Model of Disability, demonstrating how technology can remove societal barriers. It empowers blind individuals to navigate public spaces independently and access new environments confidently, showcasing that blindness, while part of one’s identity, does not hinder participation in society.
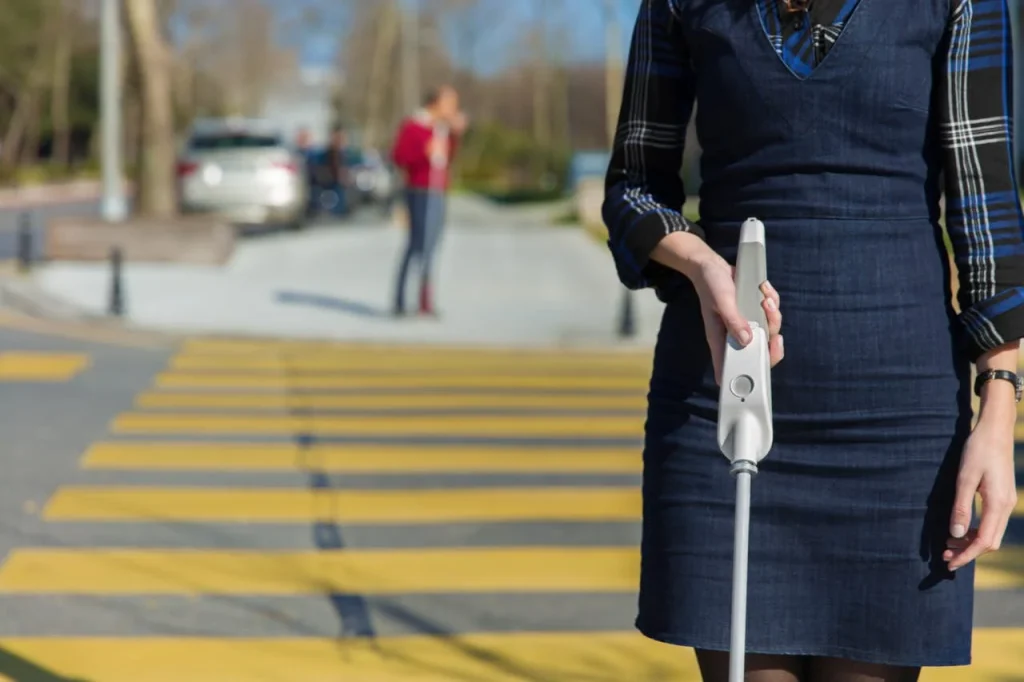

Image Source: WeWALK – EYDK
Conclusion
WeWalk is a groundbreaking assistive technology that enhances mobility and independence for people who are blind or have low vision. Its features—obstacle detection, haptic feedback, and GPS integration—demonstrate the potential for smart devices to improve accessibility. By addressing both the Social and Medical Models of disability, WeWalk empowers users and promotes inclusivity. As technology evolves, products like WeWalk will continue to play a key role in creating a more accessible world for individuals with disabilities
Sources
WeWALK Smart Cane – https://wewalk.io/en/product-details/
Models of Disability: Types and Definitions – https://www.disabled-world.com/definitions/disability-models.php