By Penghao Zhu / May 3, 2024
Client: Long Island Zoning Atlas for CUNY
Discipline: UX/UI Design, Usability Testing
Design Tool: Figma, C4D, Google Form, Zoom
Research Methods: Moderate Remote User Testing, Affinity Diagram
My Role: UX Research, UX/UI Design
Duration: 6 weeks
Team: Radhika, Manjot, Ivory, Calvin, Kacey
About the Client
The CUNY Mapping Service at the Graduate Center is part of the Center for Urban Research, which organizes basic and applied research addressing the core issues facing New York and other large cities, often in partnership with foundations, public agencies, nonprofit organizations, and other clients. The Center also trains students in research techniques and presents public forums on urban policy issues.The Mapping Service engages with foundations, government agencies, businesses, nonprofits, and other CUNY researchers to use spatial information and analysis techniques to develop and execute applied research projects. We specialize in the development of online applications that provide intuitive access to powerful data sets, displayed visually through interactive maps and in other formats.
Research Objectives
To study the overall usability of the Long Island Zoning Atlas website for promoting website visits by providing UX solutions accordingly for an enhanced user experience for professionals, organizations and non-professional individuals.
Methodology

Target User

Main Findings
Pop-up Page: 92% users skipped it
Users feel it too text-heavy, need more visual data.
Users wanted to explore the web firstly.
Professional users skip it because they already familiar with this type of website.
Visual design makes users feel like cookie pages.
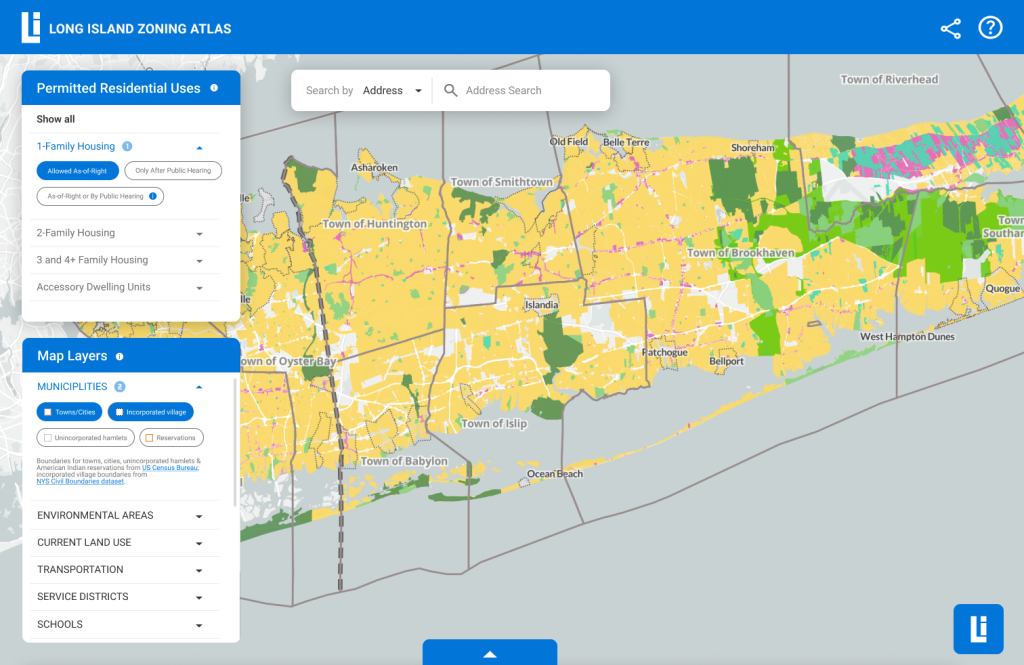
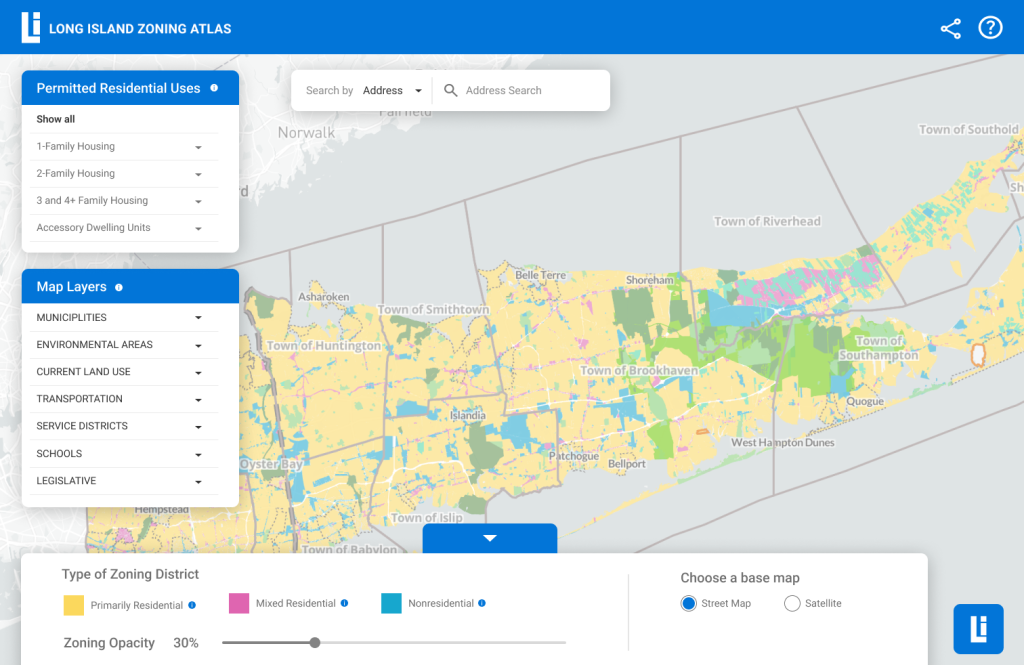
Map Page – Map Layer Filters (Left Panel)
Need to reorganize information hierarchy of filters.
Users need more filter options (eg. showing land use layers/different counties).
Need more efficiency of filter control: need to choose more than one filter at one time.
Need to see which filters are applied.
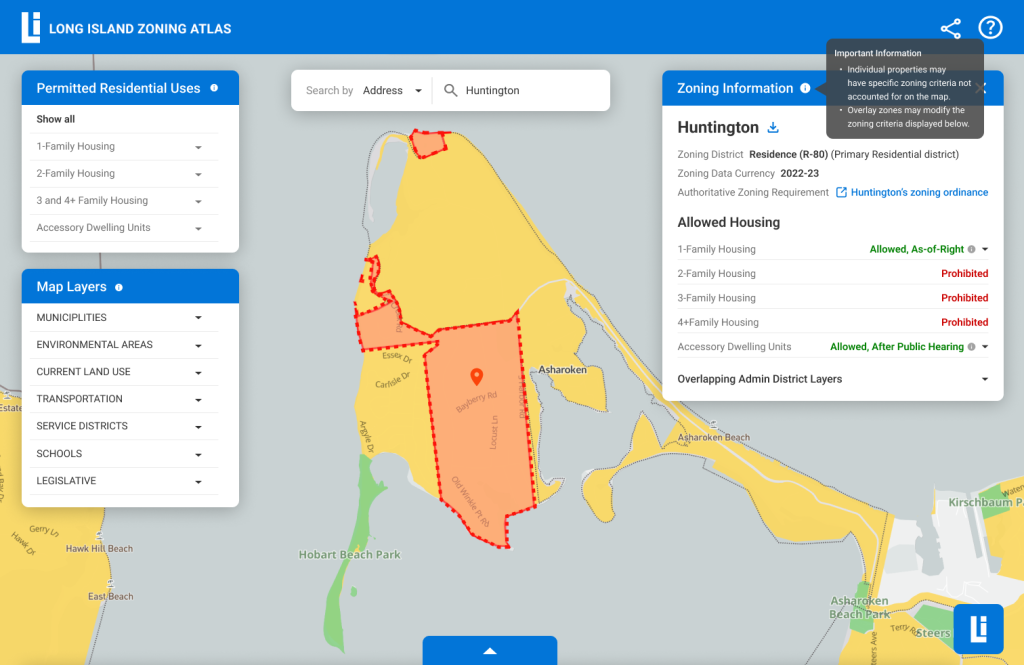
Map Page – Zoning Information (Right Panel)
Need to reorganize information hierarchy of the text.
Information of the specific zoning area is the most important to users but it’s difficult to find.
Important info doesn’t seem very useful to users, the title is too general.
Users need the sense of credibility. (eg. if the data is up-to-date, the authoritative data source)
Users need to share/download data, or be directed to the open source website to get data.

Our Solution
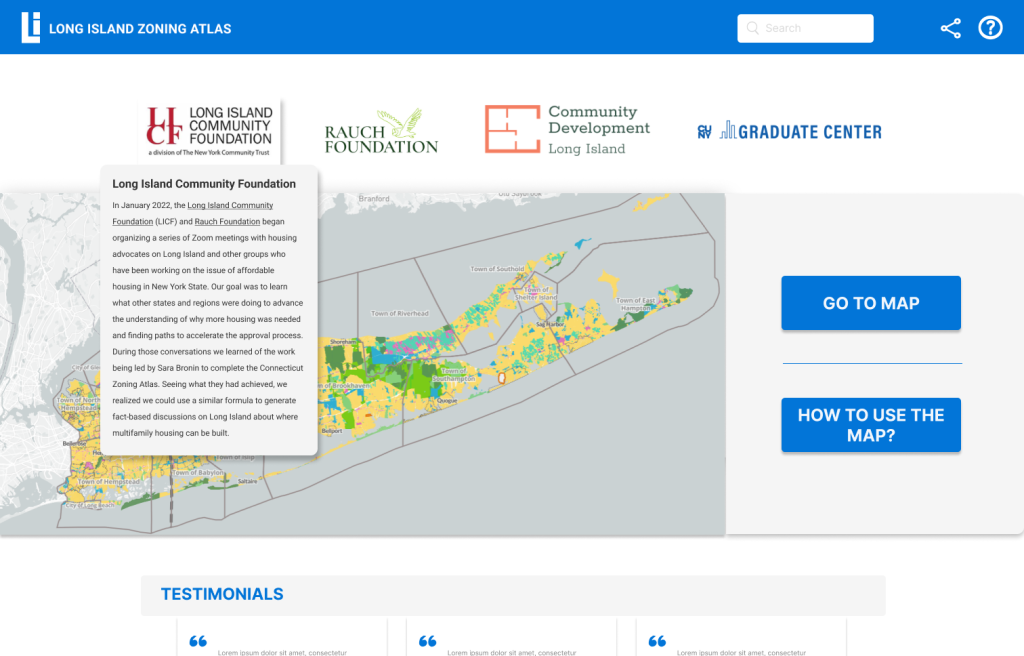
Landing Page to Showcase the Zoning Atlas Features and Key Information
Building an Landing page for the map to ease the users in the world of GIS.
This solution takes into consideration the diverse users and caters to their different needs.
Users are given agency of their actions, they can directly “Go to Map” or “How to use the Map”.
New users are easily able to see the credible source of the website, giving them the clarity of the websitess intention.
The landing page also signifies the importance of the website and the GIS data by presenting solid testimonials of the users.
Creating a footer for a website, helps the users gain holistic clarity of the website navigation.
Adding a “Contact Me” section helps users easily connect with the website team.
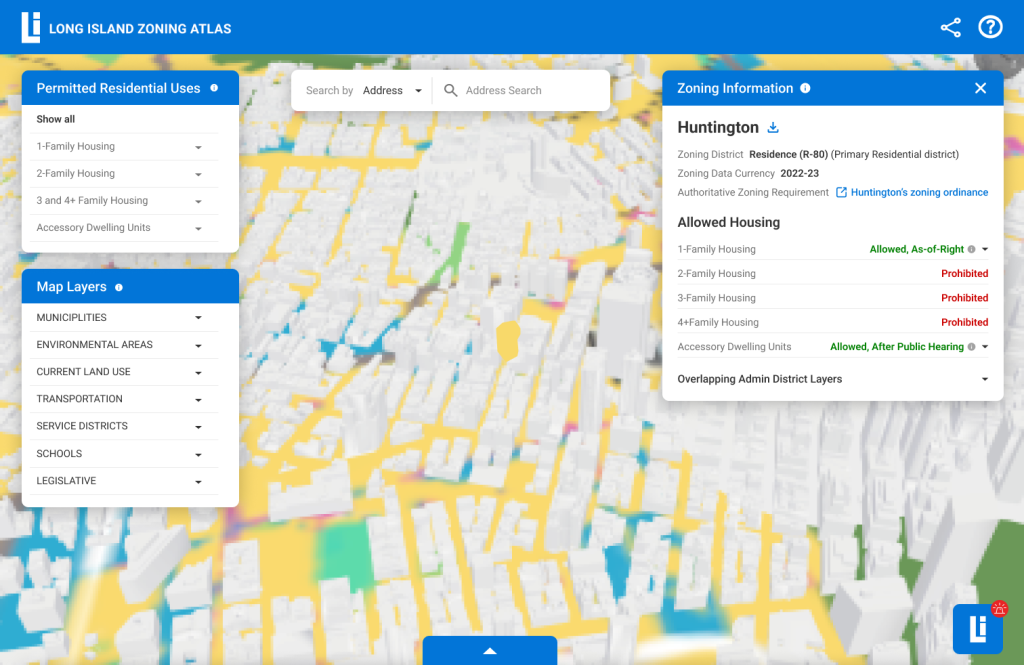
Optimize Interactive Map with Clear Prioritized Information.
Designing visually distinct sections to define different purposes of the functions.Realigning the location of the search bar to indicate the the search only functions within the map and not as a global search bar. Rein forming the location of the Types of zoning Districts from top of map to bottom of the map to visually increase the map coverage.Always having “How to use the Map” option at the top right available at the first click to help users refer to the guide.Letting “How to use the Map” open in a new window so that the map screen and data is not disturbed. Hence, users can simultaneously refer to the guide and the map without break the mental model of reopening the guide to reach to the desired information.
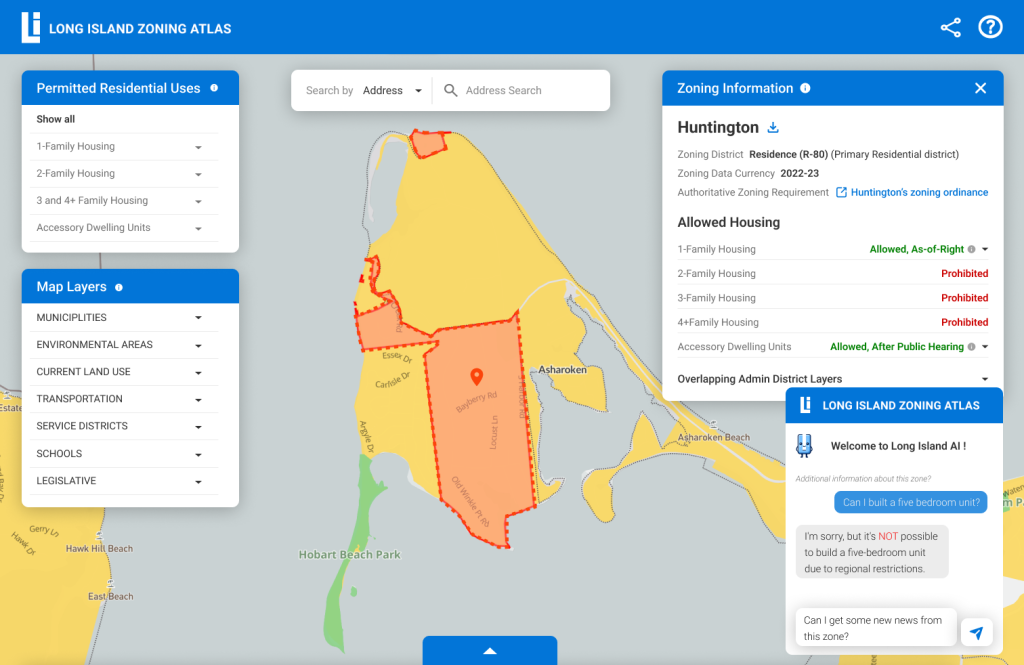
Get AI powered zoning data and statement with LI Bot
Featuring Li Bot, an AI chatbot to respond to immediate queries and information related to the zoning present within the website.
Advantages:
Prompt-based chatbots guide the conversation along predefined paths or topics, ensuring a structured interaction. This can prevent users from getting lost or frustrated in the conversation flow.
Li Bot answers from the websites’ predefined data sets to reduce risks of anomalous information.
Prompt-based chatbots can efficiently handle common queries or tasks by presenting users with quick options.
Areas of digital inclusivity, for example addressing color blindness, identifying the meanings of terminologies used across the website, etc.
Prototype

Client Presentation

